Group Martens
Crosstalk of protein aggregation and disaggregation with autophagy cargo receptors
Group Leader, Scientific Coordinator
Sascha Martens
Sascha Martens obtained his Diploma and Doctoral degrees from the University of Cologne in Germany. For his postdoctoral training he moved to the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, UK. In 2009 he established his independent laboratory at the Max Perutz Labs Vienna.
- Institute Max Perutz Labs, Univ. of Vienna
- Phone +43 1 4277 52876
- Mail sascha.martens@univie.ac.at
- Web https://www.maxperutzlabs.ac.at/martens
Projects within consortium
Autophagy is a conserved cytoplasmic degradation pathway for the degradation of harmful substances within lysosomes. This is achieved by the encapsulation of this cargo material by double membrane organelles – the autophagosomes. Among the many cargoes that are degraded by this pathway are damaged organelles, intercellular pathogens and aggregated proteins. Autophagy thereby protects us from various diseases including cancer and neurodegeneration.
Selective autophagy relies on the activity of cargo receptors, which detect the cargo, recruit the autophagy machinery for autophagosome biogenesis and finally link the cargo to the autophagosomal membrane. We focus on the role of cargo receptors and their interplay with autophagy machinery as well as other components of the proteostasis network in the degradation of fibrillar protein aggregates. A particular focus of our project is to understand why autophagy fails to degrade proteins aggregates that accumulate in neurodegenerative diseases. We therefore study if disaggregation of protein aggregates changes the way the autophagy receptors interact with them and with the autophagy machinery. We also study if disaggregation promotes proteasomal degradation of aggregated proteins and to which extent the cargo receptors influences this process. Finally, this subproject will assess how the cargo receptors and disaggregases interact with fibrillar protein aggregates in cells. To achieve our goals we combine biochemical reconstitution, cell biology, structural biology as well as mass spectrometry.
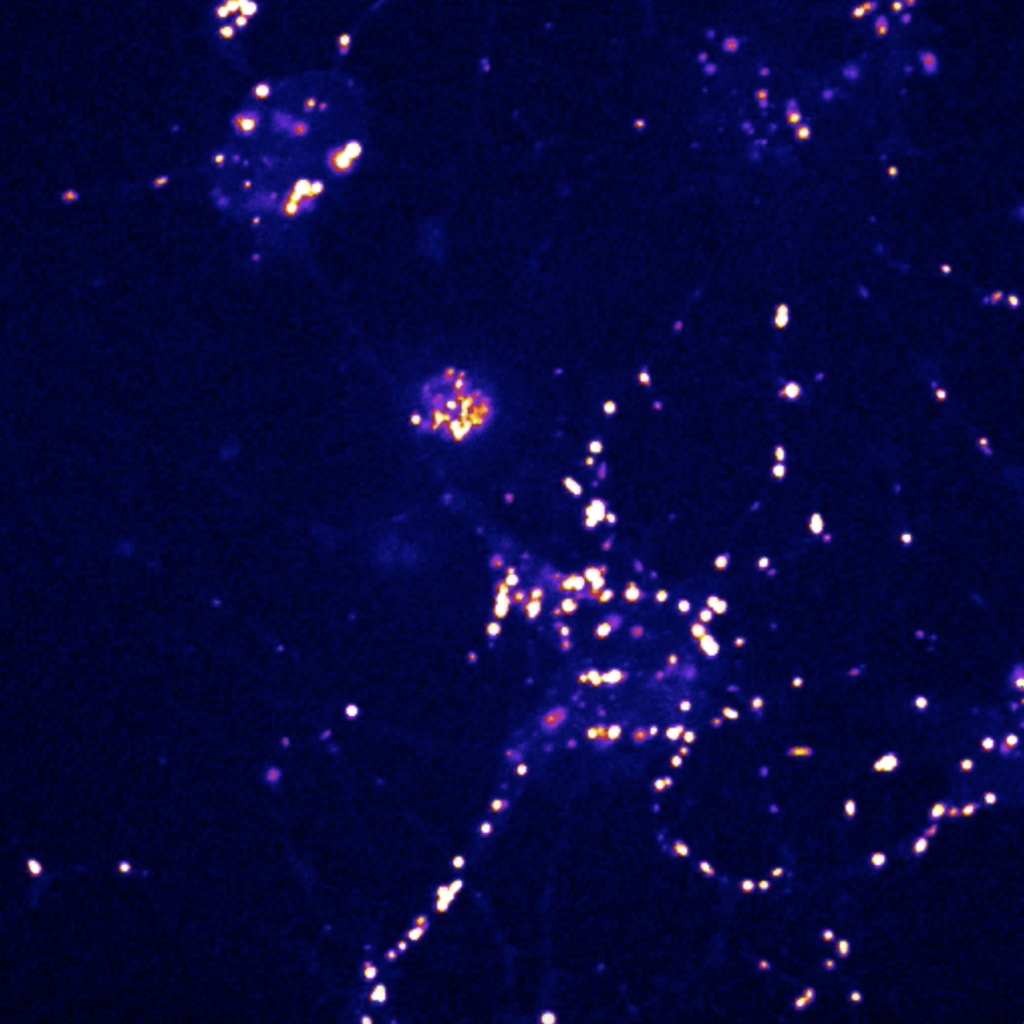
A neuron expressing an endogenously tagged cargo receptor.
Project members
-
Postdoc
Luca Ferrari
SFB Member
-
PhD Student
Bernd Bauer
Associated
-
Master Student
Maximilian Schmid
Associated
Targeted Protein Degradation related publications by Group Martens
- 2024 Tau fibrils evade autophagy by excessive p62 coating and TAX1BP1 exclusion Science Advances Go to publication →
- 2024 Large-scale chemoproteomics expedites ligand discovery and predicts ligand behavior in cells Science Go to publication →
- 2023 Sequestration of translation initiation factors in p62 condensates Cell Reports Go to publication →
- 2023 p62 and NBR1 functions are dispensable for aggrephagy in mouse ESCs and ESC-derived neurons Life Science Alliance Go to publication →
- 2023 The membrane surface as a platform that organizes cellular and biochemical processes Developmental Cell Go to publication →
- 2023 Aggrephagy at a glance Journal of Cell Science Go to publication →
- 2023 NDP52 acts as a redox sensor in PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy EMBO Journal Go to publication →
- 2023 Shuffled ATG8 interacting motifs form an ancestral bridge between UFMylation and C53-mediated autophagy EMBO Journal Go to publication →
- 2022 Orchestration of selective autophagy by cargo receptors Current Biology Go to publication →
- 2021 Reconstitution defines the roles of p62, NBR1 and TAX1BP1 in ubiquitin condensate formation and autophagy initiation Nature Communications Go to publication →
- 2020 Reconstitution of autophagosome nucleation defines Atg9 vesicles as seeds for membrane formation Science Go to publication →
- 2020 A cross-kingdom conserved ER-phagy receptor maintains endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis during stress eLife Go to publication →
- 2020 A PI3K-WIPI2 positive feedback loop allosterically activates LC3 lipidation in autophagy Journal of Cell Biology Go to publication →
- 2019 FIP200 Claw Domain Binding to p62 Promotes Autophagosome Formation at Ubiquitin Condensates Molecular Cell Go to publication →
- 2018 p62 filaments capture and present ubiquitinated cargos for autophagy EMBO Journal Go to publication →
- 2016 Mechanism of cargo-directed Atg8 conjugation during selective autophagy eLife Go to publication →
- 2015 Oligomerization of p62 allows for selection of ubiquitinated cargo and isolation membrane during selective autophagy eLife Go to publication →
- 2014 Cargo binding to Atg19 unmasks additional Atg8 binding sites to mediate membrane–cargo apposition during selective autophagy Nat. Cell Biol. Go to publication →